Unfolding Various Types of 3D Printers: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
The evolution of technology has provided us with incredible tools, one of them being 3D printers. In recent years, these devices have grown in popularity owing to their wide range of applications, from professional to personal use. In this guide, we will explore the different types of 3D printers, their mechanisms, and benefits. Expected to provide comprehensive insight to help you choose the suitable 3D printer for your needs.
Why are 3D Printers Gaining Popularity?
The world of technology never ceases to amaze and 3D printers have ridden this wave with a surge in popularity. This fascinating tool transforms a digital blueprint into a physical 3D object, broadening horizons for creativity, and innovation. Key sectors ranging from small ventures to large industries have started embracing this ground-breaking technology. But what are the reasons behind their increasing popularity? Here's why:
- Cost-Efficiency: 3D printers significantly reduce the cost of manufacturing prototypes as compared to traditional methods.
- Rapid Prototyping: The ability to create models faster than ever has facilitated speedy product development and innovation.
- Customization: 3D printers allow for the creation of tailor-made products catering to specific requirements without additional production complications.
- Reduced Wastage: Unlike conventional subtractive manufacturing, 3D printers add materials layer by layer, resulting in minimal waste production.
- Versatility: From medical equipment to architectural models, the potential applications for 3D printers are admirably diverse and wide-ranging.
What is the Basic Mechanism Behind 3D Printers?
3D Printing, also hailed as additive manufacturing, is a process whereby three-dimensional objects are built from a digital file. This operation takes place layer by layer until the object is formed. Now, let's delve into the different types of 3D printers:
Understanding Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and Its working
FDM, an extensively used type of 3D printing, functions by discharging heated material, generally thermoplastic filament. As this material cools down, it solidifies to form the object. The salient features of FDM printers are:
* Affordability: They are budget-friendly, making them a common choice.
* Ease of use: The process is easy to understand and operate.
* Wide range of material compatibility: These printers work with a vast variety of materials.
* Drawback: They don't provide the best smoothness or highest resolution compared to other types.
Enlightening on Stereolithography (SLA) 3D Printers and Their Unique Advantages
Exploring Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) Printers and Their Distinctive Features
Insights into Digital Light Processing (DLP) Printers and Their Innovative Traits
Each printer type has distinctive advantages and uses, and understanding these can help potential users choose the most suitable one for their requirements.

Conclusion
FDM is one of the most common types of 3D printers. It works by extruding heated material, usually a thermoplastic filament, which hardens upon cooling to create the object. Each layer adheres to the previous one till the complete object is formed. FDM printers are known for their affordability, ease of use, and wide range of compatible materials. However, they do not offer the highest resolution or smoothest surface finish compared to other types.
Related FAQs about what are different types of 3d printers
What are the practical uses and applications of different 3D printers?
3D printers have vast applications ranging from prototyping in industries, architectural models to personalized home items. FDM 3D printers are widely used for basic models and prototypes. SLA printers are known for detailed and precise models ideal for jewelry or dental work. SLS printers excel in producing firm and complex geometrical objects, beneficial for industries. DLP printers are known for high-speed operation, useful in mass production.
How do I decide which type of 3D printer is right for me?
Deciding on a 3D printer depends on factors like budget, precision required, material preference, and application. FDM printers are budget-friendly and user-friendly. SLA printers are ideal for high precision tasks. SLS printers work well with a variety of materials, while DLP printers are suitable when high speed is a priority.
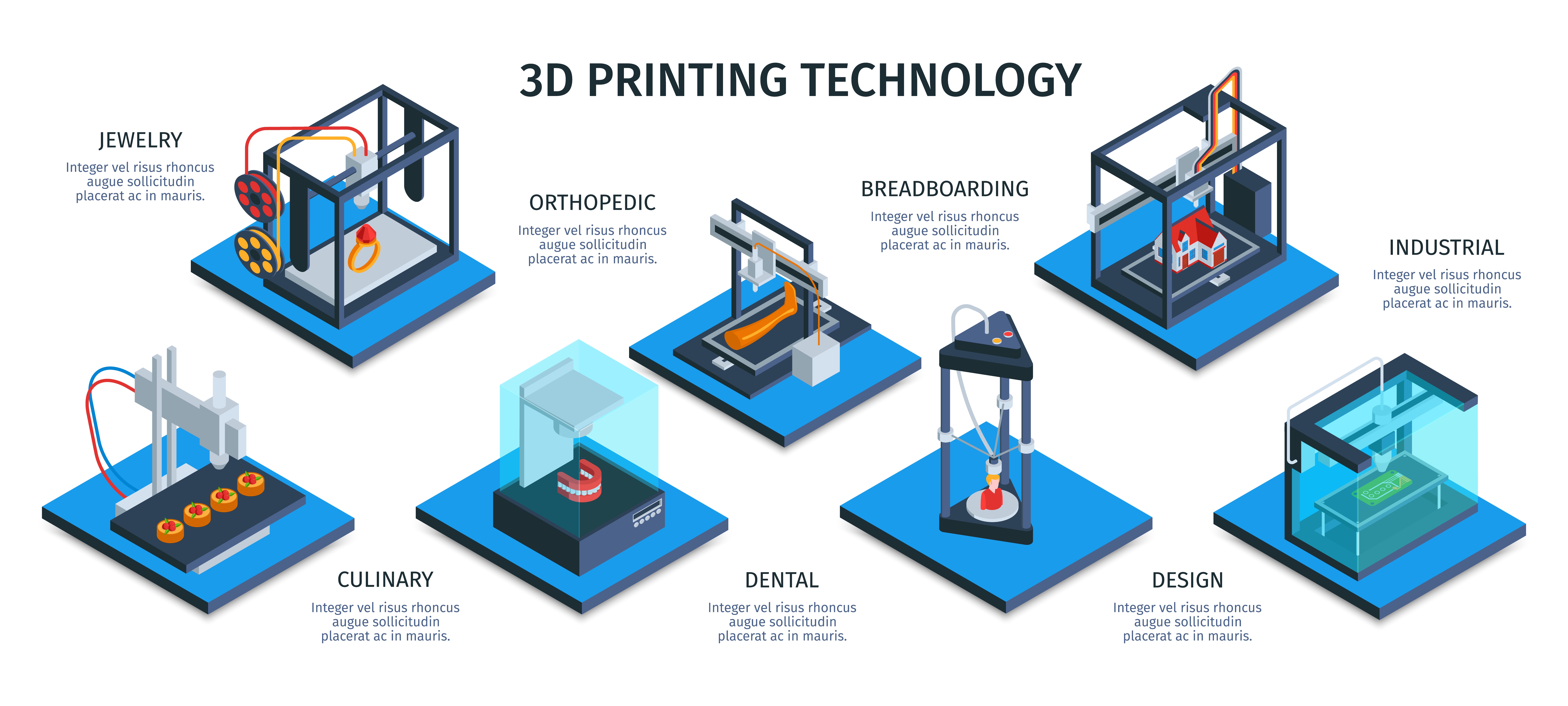
Can you highlight some of the key features and benefits of these types of 3D Printers?
FDM printers are cost-effective, user-friendly and offer a wide range of material compatibility. SLA printers stand out with their high precision and detailing capability. SLS printers can handle complex geometric designs and have wide material compatibility. DLP printers impress with their high-speed operation and quality output.


