Understanding Scanners: A Comprehensive Guide to File Formats
Introduction
Exploring the world of document scanning can seem complex, but understanding the basics of file formats can make it significantly simpler. This comprehensive guide aims not only to expound what file formats are and why they are crucial, but also to provide detailed insights into various file formats, how they work, and which one to use according to your requirements.
What Are Scanners and Why Do They Use Different File Formats?
Scanners are technological devices that play a key role in modern documentation processes. They capture and digitize images from various physical sources, including photos, posters, magazines pages, and more. This converted information then becomes editable and displayable on your computer.
Why do they use different file formats? Here are a few key points:
- Versatility: Different file formats provide distinct benefits regarding specific aspects of the scanning process. Depending on the chosen format, a user can optimize quality, file size, compatibility, and other features.
- Quality: Certain file formats are designed to maintain high-quality image data, ideal for rich, colorful, and detailed scans.
- Size: Some file formats use compression technologies to reduce the storage space needed for scans, thereby catering to users conscious about storage usage.
- Compatibility: Scanners use various file formats since not all systems or software accept every file type. A choice of formats increases the usability of the scanned file across different platforms.
Understanding the purpose of your scan helps dictate which file format best suits your needs, thereby optimizing the scanning process.
What Is the Role of File Formats in Scanning?
File formats play an indispensable role not only in scanning activities but also in the digital world at large. To understand their significance, it's essential first to comprehend what a file format is and its overall importance.
Delving into File Formats and Their Importance
In simple terms, a file format represents the unique way information gets encoded for storage in a digital file. Each type of file format has its exclusive method of storing data. Choosing an incorrect file format can adversely impact the quality of scans or create unnecessarily large files. By contrast, a correctly chosen file format ensures a balance between image quality, file size, and compatibility.
- Quality: File formats considerably impact the quality of scanned images. Some formats are specifically designed to retain high-quality images, which can be important for professional or artistic uses.
- Size: File formats significantly influence the size of the scanned files. While some formats are excellent in compressing image data to save on storage space, others are geared towards maintaining image quality without concern for file size.
- Compatibility: Not all file formats are compatible with every software. Therefore, the file format must be selected considering the software it'll be viewed or edited with.
In essence, understanding the role of file formats in scanning and choosing the appropriate one, significantly enhances the quality and efficiency of digital scanning processes.
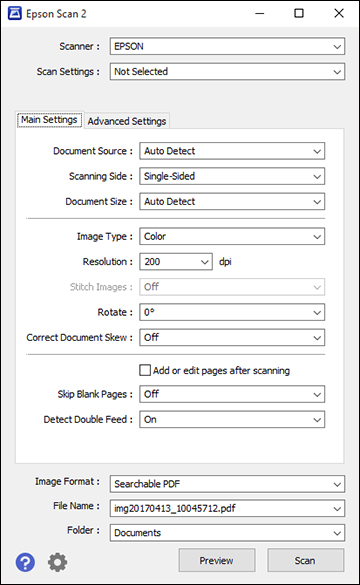
What Are the Different File Formats for Scanners and How Do They Work?
Scanners utilize an assortment of file formats, each uniquely designed to serve specific needs and uses. This variety, combining JPEG, TIFF, PDF, and PNG, extends the usability of these devices, providing an option for many different scenarios. Let's delve into each to understand their implications.
JPEG: Reshaping Scanning with Solid Compression Techniques.
- Why use JPEG for Scanning?
- JPEG, standing for Joint Photographic Experts Group, is a popular go-to format that capitalizes on a somewhat lossy compression method.
- This trait cuts down file size significantly, making it a fantastic choice for photo and document scanning offering decent quality.
- Its compressed nature facilitates easy storage and sharing, especially for digital and online distribution.
TIFF: The Bedrock of High-Quality Scanning
- What sets TIFF apart?
- The Tagged Image File Format (TIFF), is renowned for its adaptable nature and ability to retain detailed quality and image information.
- Unlike JPEG, TIFF employs lossless compression meaning it safeguards every ounce of quality.
- While TIFF files can be larger compared to other formats, it’s suitable for professional-grade image editing and printing due to its exceptional quality preservation.
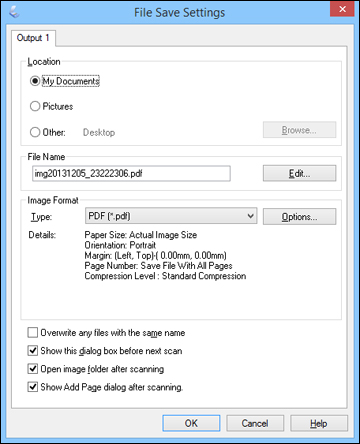
PDF: The Cornerstone of Multi-page Document Scanning
- Why lean towards PDF scanning?
- PDF, abbreviated from Portable Document Format, has found a niche in amalgamating multiple page scans into singular file entities.
- It shines in accommodating documents, reports, and books as it facilitates easy document navigation, making reading a breeze.
PNG: A High-Quality Choice for Graphics and Text Scanning
- PNG, or Portable Network Graphics, employs a lossless compression method akin to TIFF, securing it a top spot for scanning documents with text and graphics.
- PNG acts as a guardian for quality, ensuring images stay in excellent condition even through multiple saves or edits.
Every file format has unique pros and cons, with usage heavily reliant on the individual scanning need. Indeed, the combination of JPEG, TIFF, PDF, and PNG offers an astounding blend of versatility, quality, and convenience.
How to Determine the Best File Format for Your Scanning Needs?
Establishing the best file format for your scanning needs can depend on a variety of factors. You may need to consider the type of document being scanned, your requirements for image quality, the necessity for image editing, the storage space available, and the compatibility of the file with other software. To guide you effectively through this process, here are the main file formats and their key characteristics:
- JPEG (Joint Photographic Expert Group): Ideal for photos or documents where a reasonable quality is acceptable. JPEG uses a lossy compression technique which significantly reduces file size, making this format perfect for sharing and storing images online. However, repeated editing and saving may degrade the image quality.
- TIFF (Tagged Image File Format): This format is better suited for high-quality scanning since it applies lossless compression, preserving all the image quality and details. If you need professional, high-quality images for editing and printing, TIFF is an excellent choice. However, keep in mind that these files can be quite large and, as a result, may present challenges when sharing or storing.
- PDF (Portable Document Format): The PDF format is the top choice when scanning multiple pages into a single file. This format is great for scanning key documents, books, and reports.
- PNG (Portable Network Graphics): PNG is a superior choice when the focus is on images with text or graphics. Despite multiple edits and saves, the quality of a PNG image remains unchanged.
In conclusion, the choice of your scanner's file format should be based on the balance between your specific needs, the scan quality, the image sizes, and the software capabilities.
Balancing Quality, Size and Functionality: Which File Format Should I Use?
Choosing the correct file format while scanning a document involves striking the right balance between three primary aspects: quality, size, and functionality. The decision comes down to the nature of the material you intend to scan and its intended use. So, let's explore these factors to aid your decision-making process:
1. JPEG: This format is a perfect fit for scanning photos and standard quality documents, especially when they are needed for digital distribution or online purposes. Its primary advantage lies in the usage of compression technique that significantly reduces the file size. Hence, it becomes an optimal choice when your priority is sharing and storing.
- Pros: Suitable for digital distribution and storage, file size reduction.
- Cons: Compromises on quality due to lossy compression.
2. TIFF: If you aim for high-quality scanning, TIFF becomes a preferred choice. Unlike JPEG, it uses lossless compression, hence, maintaining all the quality and details of the scanned image. It is ideal for professional, high-quality image editing and printing but can give rise to sizable files.
- Pros: Maintains high-quality image, ideal for professional use.
- Cons: Large file size creates challenges in sharing or storing.
By understanding these pros and cons, you can make an informed choice about the file format that would suit your scanning needs perfectly.
Conclusion
TIFF is preferred for high-quality scanning because, unlike JPEG, it uses lossless compression. This means that it preserves all the quality and details of the scanned image. It is ideal for professional, high-quality image editing and printing. However, TIFF files can be large and may be challenging to share or store.
Related FAQs about what file format do scanners use
What file format do scanners use and why?
Scanners typically can employ a broad spectrum of file formats, including JPEG, TIFF, PNG, and PDF. The choice of format directly influences factors like image quality, file size, and compatibility, catering to different scanning requirements and ensuring optimal results.
How do different file formats impact the image quality and size?
File formats vitally influence both image quality and size. JPEG and PNG formats prioritize size and employ compression techniques, which might slightly degrade image quality. Conversely, TIFF and PDF preserves image quality and details but result in larger file size.
Are there any tips for making the right file format choice when scanning?
The choice hinges on your specific scanning requirements. JPEG is recommended for general scans and storing or sharing scans online, TIFF for high-quality images, PDF for multi-page documents, and PNG for text-rich scans ensuring image quality.


