Understanding Vulnerability Scanners: Your Guide to Enhancing Cyber Security
Introduction
With the rise of digital innovation, the risks of data breaches and cybercrime have dramatically increased. For businesses and individuals, the security of their digital assets is a top priority. One of the many facets of cybersecurity is understanding and addressing system vulnerabilities. This brings us to vulnerability scanners—tools pivotal to enhancing cyber security by identifying, assessing, and assisting in the remediation of vulnerabilities in a system. This guide delves into all you need to know about vulnerability scanners, their importance, functioning, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
Why are Vulnerability Scanners Important to Cyber Security?
In the pursuit of maintaining a secure IT environment, the role of vulnerability scanners is indispensable. Their importance in strengthening cyber security is highlighted by several crucial functions:
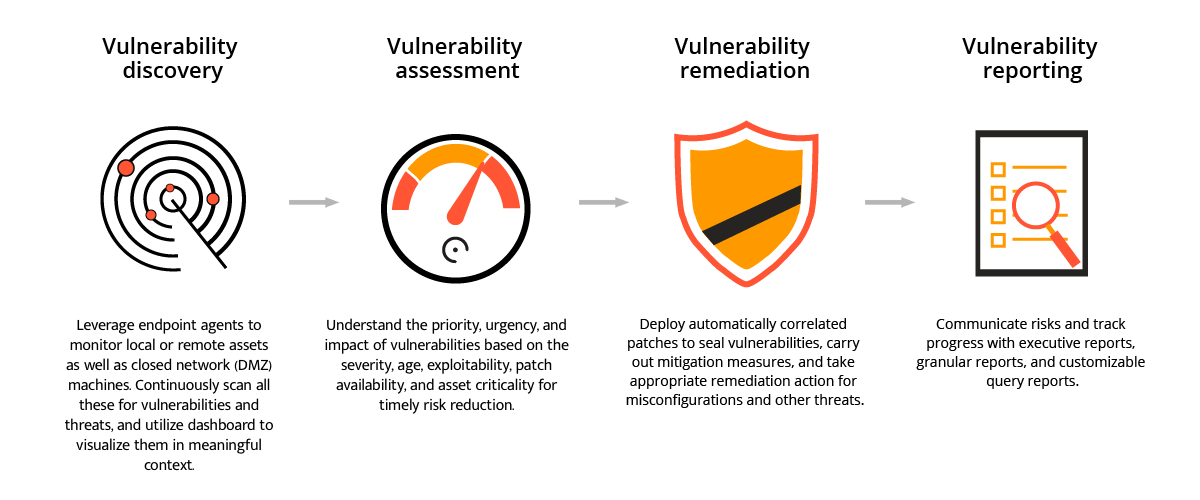
1. Proactive Security Measures: Vulnerability scanners act as a cyber security watchdog, continually scanning systems to pinpoint potential vulnerabilities - essentially the weak links in your cyber defense - that hackers can exploit.
2. Identification and Prioritization: These tools not only identify weaknesses in your system, but they also prioritize them based on their degree of severity. This allows organizations to allocate resources efficiently and address the most crucial issues first.
3. Strategic Planning: Vulnerability scanners provide thorough insights into the security posture of your network. Armed with this information, decision-makers can make strategic investments in bolstering their cyber defenses.
4. Compliance Assurance: With growing regulatory oversight on data protection, maintaining compliance has never been so important. Vulnerability scanners facilitate compliance by documenting identified vulnerabilities and the remediation steps taken.
5. Mitigation Recommendations: Lastly, an effective vulnerability scanner offers recommendations on how to address detected security loopholes. This guidance is invaluable in ensuring timely, effective mitigation of vulnerabilities.
In conclusion, the importance of vulnerability scanners in cyber security lies in their ability to give an unprecedented understanding of your cyber risk landscape, enabling you to take action based on insightful, accurate, and timely data.
What Constitutes a Vulnerability, and how Can Scanners Detect Them?
In cyber security parlance, 'vulnerability' refers to a loophole, a soft spot, or a gap in an IT system— software, hardware, or a networking system— that could potentially be exploited by cyber attackers to gain unauthorized system access or carry out malicious actions. Here are the usual sources of vulnerabilities:
- Software bugs: These are flaws due to errors in software coding, which attackers can exploit.
- Unintended system configuration: Incorrect configurations can leave the system open to attacks.
- Out-of-date software: The lack of up-to-date security patches can expose a system to vulnerabilities.
- Weak passwords: Predictable or straightforward codes can become an easy entry point for cybercriminals.
- Human error: Careless or uninformed actions by users could lead to security gaps.
Vulnerability scanners play a vital role in detecting these system vulnerabilities. They function by:
1. Gathering Info: The scanner collects information about the target system — its structure and components.
2. Comparison: It contrasts the gathered information against a database of known vulnerabilities, like the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) system.
3. Performing Checks: The scanner carries out active tests on the system to confirm the existence of vulnerabilities.
4. Identifying Gaps: The scanner scrutinizes every system component, from the operating system to the applications on it, pinpointing any security loopholes or soft spots needing patching or reinforcement.
In essence, vulnerability scanners offer a proactive defense measure against potential cyber threats by identifying and providing remedies for system vulnerabilities.
How Do Vulnerability Scanners Work?
In-depth View of the Scanning Process
The working mechanism of a vulnerability scanner can be demarcated into two main components, namely discovery and analysis.
- Discovery Phase: In this critical first step, the vulnerability scanner executes the following processes:
1. Generation of a comprehensive network map
2. Identification and listing of active devices on the network
3. Cataloging the installed operating system and software on each device
Post this, a deep scan gets executed which involves an exhaustive list of vulnerability checks. These checks are based on information accumulated in the discovery phase and involve the transmission of pings, packets, and requests to the targeted systems.
- Analysis Phase: After the discovery phase, comes the analysis stage where the scanner evaluates the responses collected to pinpoint vulnerabilities.
A Look Into the Assessment of Vulnerability Scanning Results
The assessment of the scanning process outcomes constitutes the next critical stride.
- Scoring System: Scanners predominantly use an industry-standard scoring system known as the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS). This system assigns a numerical rating to each detected vulnerability, indicating two vital parameters:
1. The potential impact of the vulnerability
2. The ease of exploitation of the said vulnerability
The final report produced by the scanner, which amalgamates all these scores, helps IT administrators discern the remediation steps for each identified vulnerability thereby bolstering the overall system security framework.
What are the Different Types of Vulnerability Scanners and How Do They Vary?
As you delve into the world of vulnerability scanners, understanding their typology becomes essential. Each type comes with unique functionalities, tailored to address specific system vulnerabilities. Let's explore the three primary kinds: network-based scanners, host-based scanners, and web application scanners.
Diving into Network-based Scanners
Network-based scanners, as their name implies, focus primarily on assessing vulnerabilities within the network. They act like an intruder attempting to penetrate your system, scanning for exploitable weak points. Their scope includes workstations, servers, network protocols, and even devices like routers and switches.
Main Features of Network-based Scanners:
• Excellent for large, complex networks.
• Primarily external-facing; designed to mimic an outsider attack.
• Can assess multiple systems simultaneously.
• Predominantly non-intrusive; rarely disrupts system’s operations.
Dissecting the Functionality of Host-based Scanners
Host-based scanners direct their attention internally, scanning individual host computers or devices for potential weaknesses. By gaining in-depth knowledge of the configurations and the installed software on each host, they can pinpoint outdated software, detect incorrect configurations and insecure software settings.
Key Points about Host-Based Scanners:
• Comprehensively scans individual hosts.
• Primarily internal-facing, effective against insider threats.
• More intrusive than network scanners, requiring administrative access.
• Provides detailed analysis of each host’s vulnerabilities.
Exploring the Uniqueness of Web Application Scanners
Web application scanners specialize in locating vulnerabilities in web applications. They can identify issues like Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), SQL Injection, and other flaws specific to web applications. With the growing importance of web-based platforms and applications, their role is becoming increasingly crucial.
Distinctive Features of Web Application Scanners:
• Tailored to handle web-based vulnerabilities.
• Detects issues like XSS, SQL Injection, etc.
• Can test both authenticated and unauthenticated parts of applications.
• Essential for businesses heavily reliant on web applications.
In conclusion, understanding the various types of vulnerability scanners enables organizations to choose a scanner (or combination of scanners) best-suited to their unique IT environment. Adequate understanding of these tools is a significant stride in achieving a robust cybersecurity posture.
How to Choose the Right Vulnerability Scanner for Your Needs?
Choosing the right vulnerability scanner is not a simple task, and necessitates an understanding of your existing network infrastructure, security requirements, and business objectives. Balance these aspects with the capabilities of your prospective scanner. Here are several key factors to consider:
1) Coverage and Compatibility: Ensure your scanner supports the technologies and platforms deployed in your IT environment. These may range from servers, workstations, web applications, databases, IoT devices, and more. A comprehensive vulnerability scanner should cover all these areas.
2) Ease of Use: Look for user-friendly vulnerability scanners that come with a simple and clear interface, intuitive configuration settings, and easy-to-understand reports.
3) Up-to-date Vulnerability Database: An ideal scanner should maintain an up-to-date database of known vulnerabilities, so it can constantly provide effective detection.
4) Scalability: Your chosen scanner should be able to grow with your business, being adaptable to changes in your network topology and size.
5) Timely and Detailed Reporting: A good scanner should offer timely results, presenting detected vulnerabilities with details like severity rating, potential impact, and remediation steps.
6) Vendor Support: Lastly, choose a product with strong vendor support, where you can receive assistance if any issues arise.
Remember, the primary goal is to find a solution that will work best for your unique needs. Make the choice that suits your business requirements today and can scale with your future aspirations.
Conclusion
There are several types of vulnerability scanners, including network-based, host-based, and web application scanners. Each of these has unique features and is used in different scenarios.

Related FAQs about what are vulnerability scanners
What is the Role of Vulnerability Scanners in Protecting Against Data Breaches?
Vulnerability scanners are integral in cybersecurity. They proactively identify, assess, and help mitigate vulnerabilities in a system, minimizing the risk of data breaches. They provide insights into your system's security posture, prioritize weaknesses based on severity, and guide in strategic planning and compliance assurance.
Can a Vulnerability Scanner Guarantee the Resilience of my System?
While a vulnerability scanner significantly enhances system resilience by identifying and assisting in remediating vulnerabilities, it doesn't provide a 100% guarantee. Additional measures, including regular system updates, user education, and implementation of robust cybersecurity policies, are crucial in fortifying system resilience.
How do Internal and External Vulnerability Scanners Differ in Functioning?
Internal vulnerability scanners are designed to identify threats within the network, focusing on individual host computers or devices. In contrast, external scanners mimic an intruder's attempt to penetrate the system from outside, identifying vulnerabilities across network protocols and devices.


