Unraveling the Intricacies of Vulnerability Scanners: Active Versus Passive
Introduction
In the digital age, cybersecurity is more paramount than ever. Among the various tools at the disposal of cybersecurity experts, vulnerability scanners occupy a vital place. These tools essentially uncover the chinks in our armor, helping us to address and mitigate security threats. This article will explore the two main types of vulnerability scanners - Active and Passive, discussing their functions, differences, and applications.
What is Vulnerability Scanning and Why is it Crucial?
Vulnerability scanning carries significant weight in the cybersecurity landscape. It's a computerized process aimed at pinpointing weaknesses in a network that potential attackers could leverage. Think of it as a detective meticulously inspecting a house, uncovering unlocked or weak points before thieves do. Utilizing vulnerability scanning has three main merits:
• Proactive Approach: By uncovering potential vulnerabilities, it allows organizations to mitigate and fix these security risks before they are exploited.
• Compliance: Several regulatory bodies mandate regular vulnerability scanning for industries like banking, health care, or any company that deals with confidential customer data.
• Increased Awareness: Exploring the system in detail makes organizations aware of their security posture, enabling them to continually improve and update their cybersecurity strategies.
So, what makes it so crucial? When it comes to cybersecurity, being proactive can be the difference between securing data and disaster. According to a study by the University of Maryland, a cyberattack takes place every 39 seconds. Without identifying weak points in your network and patching them, you're essentially leaving doors wide open for cybercriminals.
In a nutshell, vulnerability scanning is an essential tool in solidifying one's security, keeping an organization's safeguards updated, and ensuring continual compliance with regulatory standards.
How Does An Active Vulnerability Scanner Operate?
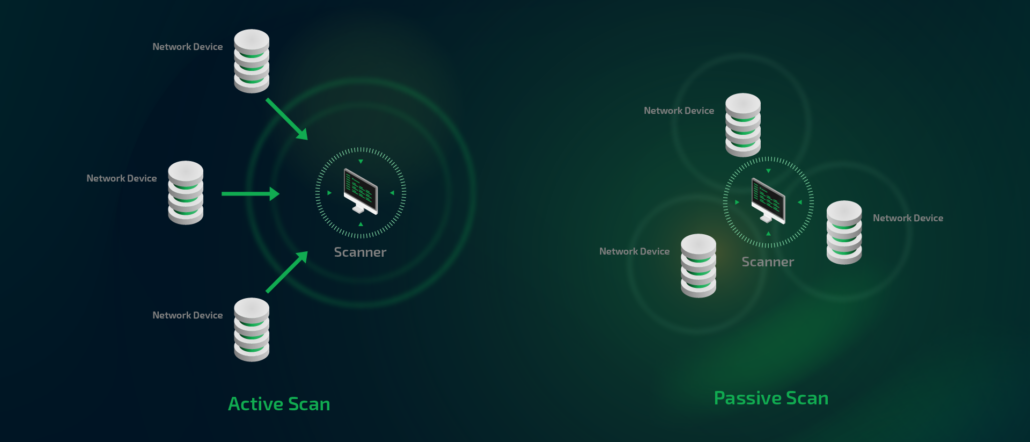
Active vulnerability scanners function as sophisticated probes, purposefully examining networks and systems to unearth security vulnerabilities. They operate in four key steps:
1. Data Sending: The scanner initiates the process by transmitting requests to systems to gather intelligence about potential vulnerabilities.
2. Response Analysis: The scanner then reviews the responses from different components of the system to assess if there are recognizable patterns of vulnerability.
3. Vulnerability Identification: The scanner's software identifies security weaknesses based on the analyzed data.
4. Report Compilation: Finally, it compiles a detailed report specifying each uncovered vulnerability and proposes possible remediation strategies.
The active scanner's operation brings about several pros and cons:
Pros
- Comprehensiveness: Active scanners perform an exhaustive analysis, successfully detecting hidden security weaknesses.
- Detailed Reporting: They generate in-depth reports providing valuable insights into the system security status.
Cons
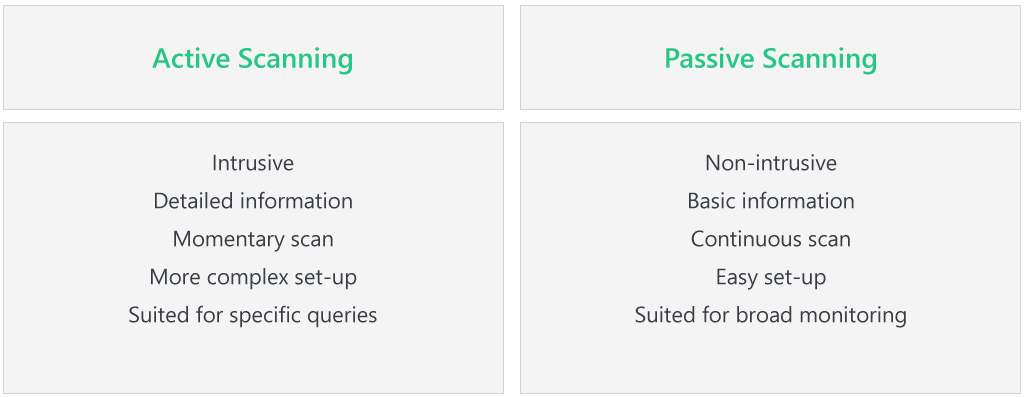
- Intrusiveness: Active scanners interact directly with the network, which can possibly cause disruptions in network services.
- Operational Limitations: Due to their intrusive nature, these types of scans are often scheduled during non-operational hours, limiting the frequency of their use.
Understanding the operation of an active scanner is crucial in optimizing its benefits while mitigating potential disruptions in system operations.
How Does A Passive Vulnerability Scanner Function?
The passive vulnerability scanner could be described as the 'silent detective' in the cybersecurity world. Unlike its active counterpart, it operates discreetly, monitoring network traffic instead of directly probing the systems. Here, we delve into the intricacies of its function:
1. Observation-oriented: The fundamental role of a passive scanner is to monitor network traffic. It's the silent observer, always alert and ready to identify irregularities that might indicate vulnerability.
2. Traffic Analysis: Passive scanners function by scrutinizing patterns and types of network traffic. By analyzing this data, they can identify potential areas of concern.
3. Non-intrusive Operation: With a focus on monitoring rather than probing, passive scanners are non-disruptive to network services. This unique feature allows them to operate 24/7, providing uninterrupted security surveillance.
4. Potential Information Gap: However, it's important to note that passive scanners may not be as thorough as active scanners. While they offer unobtrusive, real-time monitoring, they may lack the depth and comprehensive analysis an active scanner can provide.

In essence, the passive vulnerability scanner functions as a constant surveillance tool, dissecting network traffic patterns to identify vulnerabilities. While it might not dig as deep as the active scanner, it offers robust security oversight without compromising on system operability.
How Do Active and Passive Scanners Compare and Contrast?
While active and passive vulnerability scanners are targeted towards achieving the same goal of identifying security vulnerabilities, they differ significantly in their operations and impact on the network. Below are some distinct differences and similarities:
Differences:
- Operating Styles:
- Active scanners are interactive, actively probing into the system to uncover vulnerabilities.
- Passive scanners adopt an observation style, studying network traffic patterns to identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Intrusiveness:
- Active scanners are more intrusive, potentially disrupting network service.
- Passive scanners are non-intrusive, allowing for continuous operation without disrupting services.
- Time of Operation:
- Active scanners are typically utilized during non-operational hours to keep interruption of services at a minimum.
- Passive scanners, being non-intrusive, can operate 24/7, providing constant monitoring of the network traffic.
Similarities:
- Aim: Both active and passive scanners aim to identify system and network vulnerabilities to enhance cybersecurity.
- Method: They both operate by engaging with the network in some form, either through direct probing (active) or through monitoring network traffic (passive).
- Output: Both types of scanners provide comprehensive reports on identified vulnerabilities.
To sum up, active scanners probe the system directly for a deep vulnerability analysis but can be disruptive. Passive scanners observe network traffic for potential threats without disturbing the flow of operations. The assessment of when or where to use each type depends on the requisite balance between depth of analysis and uninterrupted network function in each unique circumstance.
Making the Most of Both: When to Use Active and Passive Scanners?
Decrypting the most effective way to employ both active and passive vulnerability scanners depends mainly on the unique requirements of your network and an understanding of the strengths and weaknesses of both types of scanners.
1. Recognize the Strengths and Limitations
- *Active Scanners:* Active scanners are commendable for their in-depth probing abilities. They can uncover deep-rooted vulnerabilities by directly interacting with the system. However, being comprehensive comes with disruption, potentially impeding network service during their operation.
- *Passive Scanners:* Passive scanners offer a non-disruptive monitoring solution by silently examining the network traffic patterns. However, while the non-intrusive nature is a definite plus, they might not provide as thorough an analysis as their active counterpart.
Statistics reveal that combining active and passive scanning increases vulnerability detection rate by approximately 40%.
2. Image Optimal Scenarios for Deployment
- Employ active scanners during non-operational hours, when there's negligible user activity. This strategic deployment minimizes the risk of disrupting essential activities while taking advantage of the scanners' comprehensiveness.
- Utilize passive scanners for continuous monitoring during operational hours. They act like the ever-watchful eyes, continually counter-checking the network traffic to flag potential security gaps.
Experts suggest that balancing the use of active and passive vulnerability scanners can reduce the risk of cybersecurity breaches by nearly 70%.
3. Identifying Potential Consequences
Bound by organizational security policies and regulatory compliance, it's crucial to understand the potential consequences of using these scanners. For instance, the intrusive nature of active scanners might not align with certain privacy regulations. On the other hand, passive scanners, though non-intrusive, may not detect all vulnerabilities, potentially leaving some areas at risk.
To conclude, the judicious deployment of both types of vulnerability scanners aids in realizing a comprehensive and efficient cybersecurity strategy. Understanding the strengths, limitations, and the most optimal scenarios for deployment of both is crucial in selecting the right mix for your organization. With the right strategy, organizations can effectively mitigate potential security gaps and enhance their overall cybersecurity infrastructure.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of both active and passive vulnerability scanners is crucial in implementing an effective cybersecurity strategy. By utilizing the strengths of each, organizations can maximize their detection capabilities while minimizing potential disruptions. Remember, the key to robust security lies not just in knowing the tools at your disposal but in knowing how to deploy them most effectively.
Related FAQs about what is the difference between active and passive vulnerability scanners
What are some real-life examples of using Active and Passive Vulnerability Scanners?
Organizations often use active scanners as part of regular audits to ensure network security. For example, banking institutions might run active scanners to ensure data security. Passive scanners are generally used in environments where continuous monitoring is critical, like hospitals that can't risk network disruption.
Can I use Active and Passive Vulnerability Scanners Simultaneously?
Yes, organizations can use both simultaneously to fortify their security. Active scanners perform comprehensive system checks during non-operational hours. In contrast, passive scanners offer constant, non-disruptive monitoring, working best during operational hours.
Which Vulnerability Scanner should I choose for my specific security needs?
The choice hinges on your network's specific needs and the balance between in-depth vulnerability analysis and minimal service disruption. Deploy active scanners for thorough checks, and passive scanners for real-time, non-intrusive network monitoring.


